libvpx的使用方法简析 - simple_decoder.c
/*
* Copyright (c) 2010 The WebM project authors. All Rights Reserved.
*
* Use of this source code is governed by a BSD-style license
* that can be found in the LICENSE file in the root of the source
* tree. An additional intellectual property rights grant can be found
* in the file PATENTS. All contributing project authors may
* be found in the AUTHORS file in the root of the source tree.
*/
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
# 开头自带的说明书
// Simple Decoder
// ==============
//
// This is an example of a simple decoder loop. It takes an input file
// containing the compressed data (in IVF format), passes it through the
// decoder, and writes the decompressed frames to disk. Other decoder
// examples build upon this one.
//
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
这个案例的功能是读取一个IVF格式的输入文件,解码之后把帧写到磁盘上。
// The details of the IVF format have been elided from this example for
// simplicity of presentation, as IVF files will not generally be used by
// your application. In general, an IVF file consists of a file header,
// followed by a variable number of frames. Each frame consists of a frame
// header followed by a variable length payload. The length of the payload
// is specified in the first four bytes of the frame header. The payload is
// the raw compressed data.
//
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
IVF格式的详情不是本示例的重点。
// Standard Includes
// -----------------
// For decoders, you only have to include `vpx_decoder.h` and then any
// header files for the specific codecs you use. In this case, we're using
// vp8.
//
2
3
4
5
6
为了调用解码器,需要引入vpx_decoder.h。
// Initializing The Codec
// ----------------------
// The libvpx decoder is initialized by the call to vpx_codec_dec_init().
// Determining the codec interface to use is handled by VpxVideoReader and the
// functions prefixed with vpx_video_reader_. Discussion of those functions is
// beyond the scope of this example, but the main gist is to open the input file
// and parse just enough of it to determine if it's a VPx file and which VPx
// codec is contained within the file.
// Note the NULL pointer passed to vpx_codec_dec_init(). We do that in this
// example because we want the algorithm to determine the stream configuration
// (width/height) and allocate memory automatically.
//
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
初始化解码器的函数是vpx_codec_dec_init()。
使用哪个解码器接口是在VpxVideoReader和vpx_video_reader_开头的几个函数里面判断的。具体情况不在本示例的讨论范围内,本示例中解码器信息就包含在文件里面。
NOTE:示例中vpx_codec_dec_init()的第三项是解码器配置,本案例中传入的是空指针,这样可以让它自己判合适的配置和分配内存空间。
// Decoding A Frame
// ----------------
// Once the frame has been read into memory, it is decoded using the
// `vpx_codec_decode` function. The call takes a pointer to the data
// (`frame`) and the length of the data (`frame_size`). No application data
// is associated with the frame in this example, so the `user_priv`
// parameter is NULL. The `deadline` parameter is left at zero for this
// example. This parameter is generally only used when doing adaptive post
// processing.
//
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
当帧被读入内存之后,调用vpx_codec_decode就可以对其进行解码。
这个vpx_codec_decode接受一个帧数据指针(frame)和帧尺寸(frame_size),其他一些可有可无的调节参数(user_priv)不在本案例的讨论范围,直接设空。本案例中的deadline参数设为0,这个参数主要用于自适应。
// Codecs may produce a variable number of output frames for every call to
// `vpx_codec_decode`. These frames are retrieved by the
// `vpx_codec_get_frame` iterator function. The iterator variable `iter` is
// initialized to NULL each time `vpx_codec_decode` is called.
// `vpx_codec_get_frame` is called in a loop, returning a pointer to a
// decoded image or NULL to indicate the end of list.
//
2
3
4
5
6
7
每次调用vpx_codec_decode都可能产生多个解码帧,调用vpx_codec_get_frame获取这些帧。
vpx_codec_get_frame的第二个参数接受一个迭代器指针,vpx_codec_get_frame会以迭代的方式输出解码后的帧。
// Processing The Decoded Data
// ---------------------------
// In this example, we simply write the encoded data to disk. It is
// important to honor the image's `stride` values.
//
2
3
4
5
本示例中,解码之后的数据直接写进文件里。
// Cleanup
// -------
// The `vpx_codec_destroy` call frees any memory allocated by the codec.
//
// Error Handling
// --------------
// This example does not special case any error return codes. If there was
// an error, a descriptive message is printed and the program exits. With
// few exceptions, vpx_codec functions return an enumerated error status,
// with the value `0` indicating success.
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
vpx_codec_destroy用于清理。
本示例中没有什么特殊的需要处理的错误。
# 正文开头
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "vpx/vpx_decoder.h"
#include "../tools_common.h"
#include "../video_reader.h"
#include "./vpx_config.h"
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
一堆include不用多讲。
static const char *exec_name;
void usage_exit(void) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: %s <infile> <outfile>\n", exec_name);
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
2
3
4
5
6
这是一个输出错误并退出程序的函数,用在接下来会经常见到的die函数里面,就是输出一些错误而已,不用太在意。
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
主函数开始。
int frame_cnt = 0;
FILE *outfile = NULL;
vpx_codec_ctx_t codec;
VpxVideoReader *reader = NULL;
const VpxInterface *decoder = NULL;
const VpxVideoInfo *info = NULL;
exec_name = argv[0];
if (argc != 3) die("Invalid number of arguments.");
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
一堆后面要用到的变量定义。
# 打开待解码的文件
reader = vpx_video_reader_open(argv[1]);
if (!reader) die("Failed to open %s for reading.", argv[1]);
if (!(outfile = fopen(argv[2], "wb")))
die("Failed to open %s for writing.", argv[2]);
2
3
4
5
打开文件,生成VpxVideoReader。这个输入参数argv[1]是要待解码文件的文件名,argv[1]是放解码后数据的文件的文件名。
info = vpx_video_reader_get_info(reader);
这个函数的定义里面只有一句话:return &reader->info😂。
# 获取所需的解码器
decoder = get_vpx_decoder_by_fourcc(info->codec_fourcc);
if (!decoder) die("Unknown input codec.");
printf("Using %s\n", vpx_codec_iface_name(decoder->codec_interface()));
2
3
4
这个函数顺着一查,发现下图:
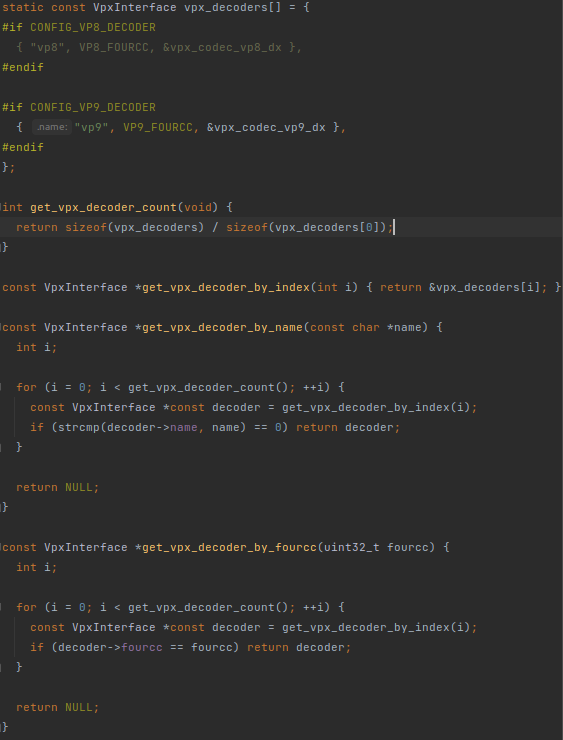
get_vpx_decoder_by_fourcc调用了get_vpx_decoder_by_index,而get_vpx_decoder_by_index直接从一个列表里选出了一个解码器。从这列表看,这就是在选vp8还是vp9。
返回值都是VpxInterface类型,说明vp8和vp9的decoder都是继承的同一个接口类。那看看这个VpxInterface又是什么:
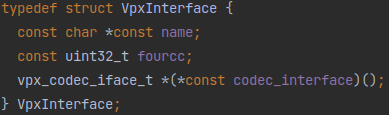
嗯,上面那个vpx_decoders[]数组和这个类定义是一一对应的。这VpxInterface里面前两个一看就是两个Metadata,最后这个vpx_codec_iface_t *(*const codec_interface)()应该就是重点。
定义看着有点复杂,这就是个函数指针。变量名是codec_interface,接受返回值是vpx_codec_iface_t *,无输入参数的函数。
那这个vpx_codec_iface_t又是什么?找找:
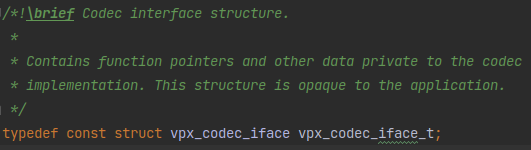
一个typedef😂,好吧,再找这个vpx_codec_iface:
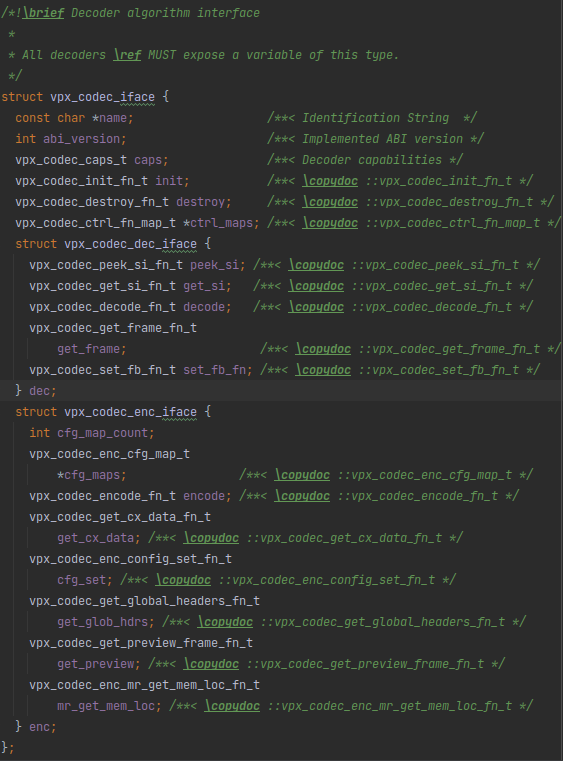
这应该就是vp8和vp9的统一接口了。这里面这些类型随便点进去几个,发现它们都是在vpx/internal/vpx_codec_internal.h里面定义的函数指针类型。哇,简单粗暴,确实称得上是“接口”。
那么再回去看vpx_decoders[]数组里的值,codec_interface对应的是这个vpx_codec_vp8_dx和vpx_codec_vp9_dx,显然这两个就是返回值是vpx_codec_iface_t *且无输入参数的函数,也是解码器的主要部分。
那看看这个vpx_codec_vp8_dx和vpx_codec_vp9_dx是什么:
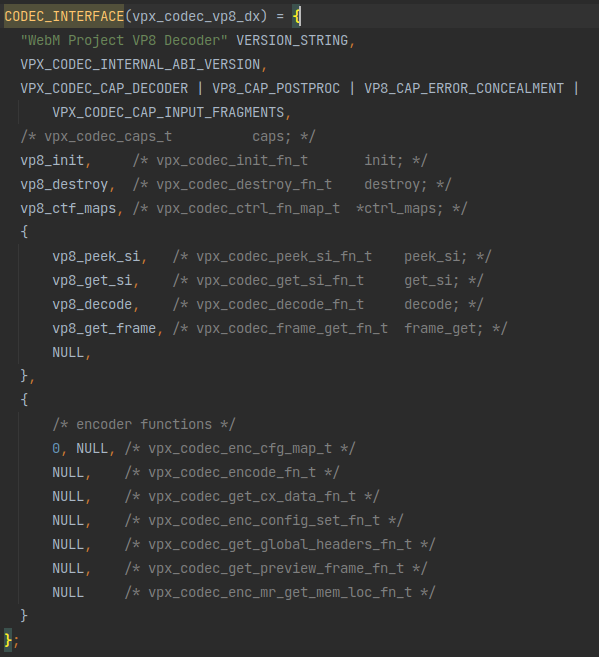
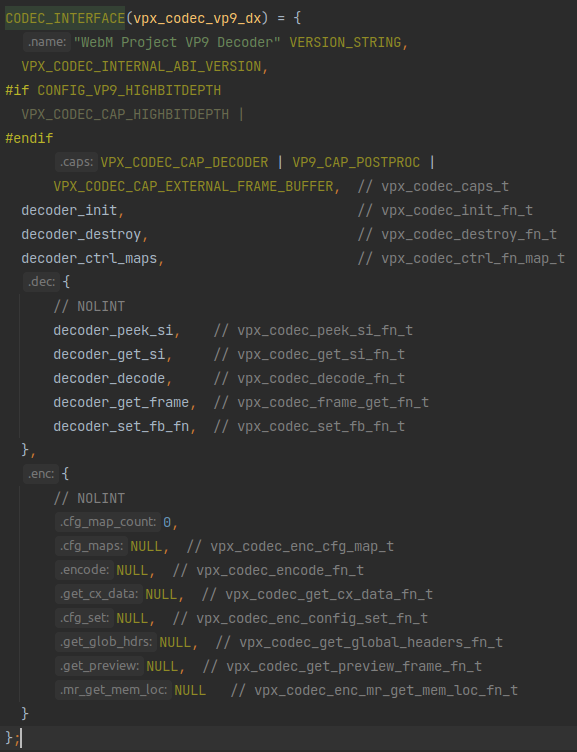
哇这个赋值,显然这就是在给vpx_codec_iface里的函数指针变量赋值,那被赋的这些值就是vp8和vp9解码器的具体实现了,记下来以后慢慢看。
还记得vpx_codec_vp8_dx和vpx_codec_vp9_dx的类型吗?它们应该是返回值是vpx_codec_iface_t *且无输入参数的函数,但这里看怎么像是在给vpx_codec_iface_t赋值?注意到vpx_codec_vp8_dx和vpx_codec_vp9_dx都被一个宏CODEC_INTERFACE包裹着,那看看这个宏是什么:
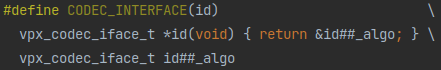
哇,秒懂,赋值之后放进函数里。一个小trick而已,和《pion/interceptor浅析》里介绍的RTCPReaderFunc之流差不多的想法。
# 初始化解码器
好了,继续看示例的代码:
if (vpx_codec_dec_init(&codec, decoder->codec_interface(), NULL, 0))
die("Failed to initialize decoder.");
2
开头的说明里讲过的初始化操作。看着像个函数,其实是被套了个宏的函数:
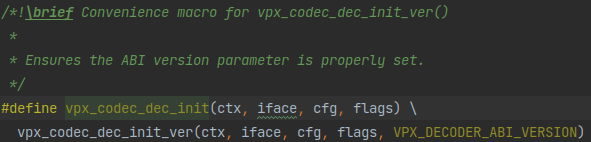
被套的函数是这个:

套个宏就是替换最后一个变量用于ABI版本检查。
初始化函数的核心就是给这个上下文变量ctx赋了一堆值,还调用了传进来的iface里面的init函数,这就是vpx_codec_iface里的函数之一,前面介绍过,不用多讲。
这个ctx是传进来的结构体指针,所以调用这个函数之后,在函数外面用户就可以用赋好值的ctx进行各种操作了。
# 解码过程
继续看示例:
while (vpx_video_reader_read_frame(reader)) {
上来就是直接一个while循环,这个vpx_video_reader_read_frame长这样:
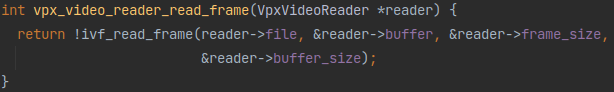
看来就是个ivf读取器啊,看样子是根据reader里的文件信息把文件数据写进reader->buffer里
vpx_codec_iter_t iter = NULL;
vpx_image_t *img = NULL;
size_t frame_size = 0;
const unsigned char *frame =
vpx_video_reader_get_frame(reader, &frame_size);
2
3
4
5
while循环里每轮来一个vpx_video_reader_get_frame,这个vpx_video_reader_get_frame也很简单:
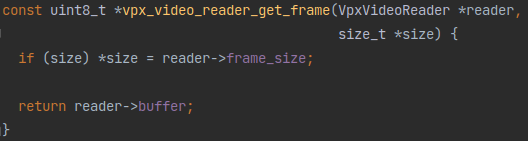
就直接返回vpx_video_reader_read_frame里写入的reader->buffer然后把数据长度传给frame_size。看这个frame的类型应该就是个unsigned char数组,看来这个libvpx里的压缩帧数据没有专门指定数据类型。
if (vpx_codec_decode(&codec, frame, (unsigned int)frame_size, NULL, 0))
die_codec(&codec, "Failed to decode frame.");
2
vpx_video_reader_read_frame之后就是vpx_codec_decode对帧数据进行解码。这个vpx_codec_decode依然很短:
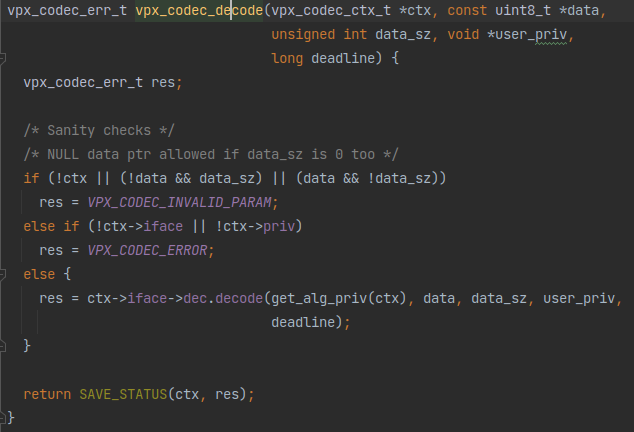
其实就是在调用vpx_codec_iface接口里定义好的解码函数dec.decode。
while ((img = vpx_codec_get_frame(&codec, &iter)) != NULL) {
vpx_img_write(img, outfile);
++frame_cnt;
}
2
3
4
最后就是一个vpx_codec_get_frame获取到解码出来的帧。这个传入的。注意到有个传入的迭代器参数iter在前后都没有用到,看来只是为了提供一点内存空间(既然外面用不到为什么还要这样定义?应该是有别的用处吧)iter只传入了vpx_codec_get_frame却没有其他任何操作。这个参数是历史遗留问题,具体可以看decoder_get_frame函数里面有一段注释的解释,《libvpx再深入一点》的解析里也有。
这个vpx_codec_get_frame依旧很短:

和vpx_codec_decode差不多,封装了一下vpx_codec_iface接口里定义好的dec.get_frame。
}
解码过程结束。
# 一些收尾操作
printf("Processed %d frames.\n", frame_cnt);
if (vpx_codec_destroy(&codec)) die_codec(&codec, "Failed to destroy codec");
2
关闭解码器。
printf("Play: ffplay -f rawvideo -pix_fmt yuv420p -s %dx%d %s\n",
info->frame_width, info->frame_height, argv[2]);
vpx_video_reader_close(reader);
fclose(outfile);
2
3
4
5
6
关闭文件读取器。
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
退出。
# 完
}
2
主函数结束
